- Jan 31
- AddictionDrug Addiction Treatment
Compulsive gambling affects about 5 million U.S. residents. Consistent compulsive gambling can quickly lead to a gambling addiction, also known as pathological gambling. While it might sound easy to stop before the problem reaches that point, the way that gambling affects your brain chemistry can make it challenging to quit.
Below, you’ll discover the science behind why so many American adults gamble compulsively, including how gambling affects the brain and how casinos manipulate players into gambling more. Keep reading to learn the physiology and psychology behind pathological gambling, along with how to handle problematic gambling behaviors.
Gambling’s Effect On Your Brain
Compulsive gambling shows signs of measurable changes in your brain chemistry. As a behavioral addiction, gambling addiction is closely connected with how the brain’s reward system functions. Specifically, the effect that gambling has on your brain’s levels of dopamine — a chemical messenger that causes feelings of pleasure — is what makes gambling so addicting.
Hitting the jackpot releases dopamine, generating exceptionally good feelings each time a gambler wins. Once you’ve experienced the rush of dopamine brought on by a gambling win, you’ll do almost anything to experience that same amount of pleasure again.
The dopamine release from gambling makes it easy to gamble repetitively without a second thought. Before you know it, gambling can become a habit and an addiction. Those with a severe gambling addiction can even get caught up in the “dark flow” — a trance-like state in which players get absorbed into a gambling game for hours.
However, as someone gambles more and more, their brain begins to build up a tolerance for the dopamine released by gambling. Over time, the brain’s reward system gets overused, and betting the exact amounts does not produce the rush of good feelings that it once did. When the brain’s reward system is blunted, those craving more dopamine must take bigger and bigger risks to achieve the same high.
Once a gambling addiction reaches this point, people will struggle to stop placing bets. Since gambling triggers the same dopamine release as using a drug, compulsive gamblers can also experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop. In these cases, people need professional help and support to recover from their addiction.
Inside the Brain of a A Person Addicted to Gambling
To understand the brain activity that occurs within problem gamblers, you’ll need a better picture of how gambling affects certain brain regions. Both animal studies and human-subject studies have found that the level of activity in certain parts of the brain can directly influence gambling behaviors.
The two main areas of the brain that impact gambling habits include:
- The prefrontal cortex: The front portion of your brain that controls planning, complex problem-solving, personality and processing potential consequences
- The ventral striatum: The portion of your brain that processes rewards and emotions like happiness
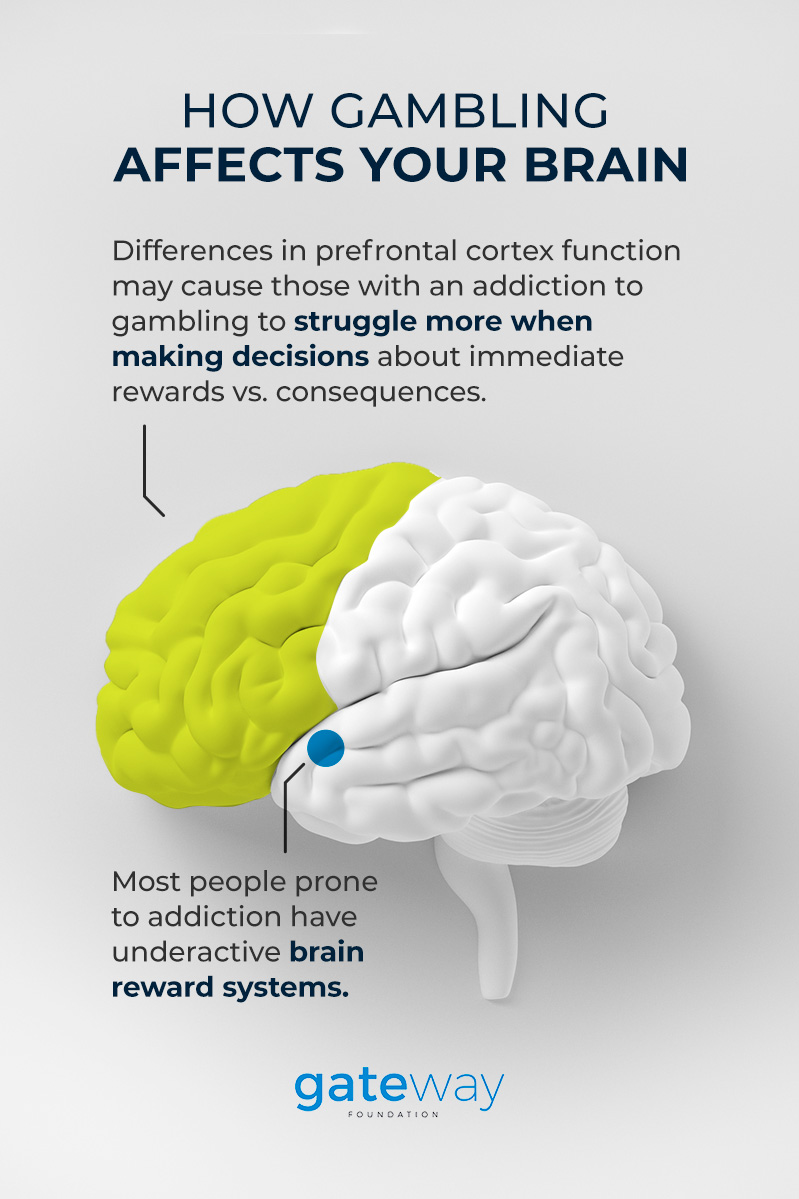
Scientists found that those with a gambling or substance use disorder experience increased connectivity to the reward system and decreased activity to the prefrontal cortex. The reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex may also explain why those with a gambling disorder tend to have more difficulty controlling their impulses than other people.
These findings indicate that individuals with problematic gambling behavior may have differences in their prefrontal cortex functioning, causing them to struggle more when making decisions about immediate rewards vs. later rewards and the consequences. Because they don’t always consider the costs of gambling, compulsive gamblers can quickly dig themselves into a hole.
Similarly, the ventral striatum part of the brain is also less active for problem gamblers. Although it might seem counterintuitive that people addicted to the thrill of gambling have lower activation in their brains’ reward pathways, it makes more sense in terms of the reward deficiency model.
The reward deficiency model proposes that most people prone to addiction have underactive brain reward systems, which draws them to engage in various reward-stimulating activities like gambling or using a substance. These findings suggest that the primary interest for those battling a gambling addiction is making up for the lack of reward system activity and positive feelings, not the money itself.
How Casinos and Games Are Designed to Keep You Gambling
In addition to the physiological factors that may push you to keep gambling, everything about casinos is deliberately designed to make people bet past their limits. Because casino owners want to get as much money as possible from people, they’ll do whatever it takes to keep people playing. By using specific game designs, layouts and other strategies, casinos naturally nudge us to gamble more.
Being in an environment that promotes problem gambling traps anyone prone to compulsive gambling. However, if you pay attention, you’ll start to notice the subtle psychological tricks used throughout casinos. Below, you’ll discover the top tactics casinos use to create the perfect gambling setting.
Game Design
Clever game design is one of the best weapons casinos have for creating games people want to keep playing. Although you might consciously recognize that casinos set up games with the house advantage, well-designed games send subconscious messages that make you ignore that logic and keep playing despite losing.
The gambling industry knows how to prevent infrequent winners from walking away by designing games that make you feel like you’re winning even while you’re losing. In recent years, casinos upgraded slot machines from old mechanical arms and reels to more technologically advanced electronic gaming machines.
Along with more attractive colorful lights and a wider range of fun sound effects, these new computerized game machines and online slots can feature more reels. Multi-line video slot machines enable players to place more bets per spin. Players can place the maximum number of bets on each spin to increase their chances of a win.
Following this maximum bet strategy allows players to win some lines while losing on others, ultimately gaining less money than their original wager. However, each time players win a line, the machine lights up and makes sounds of victory, despite losing money overall. These games disguise players’ losses as wins.
These faux wins trick players into feeling like a winner even though they just lost money, leading them to overestimate how much they truly won. The higher frequency of wins that multi-line slot machines provide also stimulates the brain’s reward system more than regular slot machines. Whether the wins are real or fabricated, the brain responds by releasing dopamine, making the game feel more enjoyable.
This false sense of winning combined with increased brain activity can be the perfect recipe for addiction. If people aren’t careful, they can easily become wholly absorbed in playing multi-line slot machines for hours on end.
Near Misses
Along with frequent mini wins, electronic gambling machines make it easier for game designers to make near misses occur more often. By programming certain outcomes onto a set of virtual reels, the house can stack the deck to make one of the reels stopping just shy of aligning for a jackpot more common. These instances are known as near misses.
Because near misses are almost wins, they stimulate areas of the brain that typically respond to wins. Activating the brain’s reward system can increase a player’s desire to keep playing the game, especially if they already struggle with problem gambling. In fact, near misses can trigger a more powerful urge to keep playing than winning.
Near misses offer a strong incentive to keep playing because they trick people into thinking the next round will finally be their chance to win. The highly motivating nature of near misses increases player commitment to a game, making the average player stay at a game longer than they intended. In fact, the measure of the dopamine response to a near miss correlates closely with the severity of a gambling problem.
The Sounds and Lights of Games
The sounds and lights of casino games include deliberately encourage gamblers to keep playing. Game designers know that gambling is more than just winning and losing — it’s an immersive experience made complete by an environment of flashing lights and striking sounds. Even a gambling app or game on a smartphone has enough visual frills and sound effects to capture users’ attention for a lengthy period.
However, it’s crucial to recognize that these amusing sounds and lights are more than just fun effects. Research shows that bright lights and sounds become more attractive and trigger more urges to gamble when combined with reward uncertainty. This type of environment keeps people gambling longer and playing faster.
Specifically, cues associated with winning, such as flashing lights and jingles, increase excitement and cause gamblers to overestimate how frequently they’re winning. When players think they’re winning more than they actually are, they assume they have enough money to keep playing.
Casino Layout
Casino owners want you to start gambling as soon as you walk in, and they design their casinos accordingly. The idea behind a casino’s layout is to lure people into playing from the moment they arrive. To accomplish this goal, most casinos have playing stations situated immediately inside their entrance, making the games as accessible as possible for players.
Although old casino layouts crammed as many gambling activities as would fit into small, boxy rooms, modern casino layouts incorporate big, open spaces with plenty of opportunities to take a breather. The idea is that allowing people to take a break from the concentration and sensory overload involved with gambling will keep them playing longer.
Creating a pleasant environment with a large lobby or bar area where people can revitalize their spirit prevents them from getting burnt out on gambling too early. The relaxed layout full of easy-to-navigate spaces that most modern casinos use makes for a more relaxed setting, making gamblers more inclined to stay and place riskier wagers.
Casino Lighting and Atmosphere
Similar to the layout, casinos put a lot of thought goes into the lighting. Back in the day, most casinos had no windows or clocks so that players would lose track of time and gamble all day. However, modern technology thwarted this strategy by giving anyone with a cellphone easy access to a handheld clock at all times.
Nowadays, many casinos have large windows with plenty of natural lighting to make players feel more comfortable. This tactic coincides with the overarching goal of the casino’s layout to create a relaxed atmosphere that people want to spend their time. Making players feel more at ease will encourage them to keep betting bigger.
In addition to visual appeal, casinos pander to the other senses. For example, one study about aromas found that wafting certain smells through a casino’s ventilation system could increase play at slot machines by 46%. The reasoning behind this increased play could be that pleasant smells make passersby slow down for a moment, notice the nearby machines and start playing.
Playing With Tokens and Chips
Although there are many reasons why casinos use tokens and chips instead of cash, the main reason is the psychological effect tokens and chips have on players. For most adults, it is far easier to part with a chip than to part with an actual bill. The bill carries more economic weight to gamblers, even though the chip symbolizes the same amount of currency.
Many players already consider tokens and chips as paid for, making them more willing to part with them. Because the player already planned on spending the chip on a game, they hardly think twice before giving it away.
Proving Skill
Even though gambling is a game of chance and pure luck, game designers are experts at making them feel like a battle of skill. Games of chance are programmed to hook players for as long as possible before eventually allowing them to walk away under the impression that they did better than chance. This false impression fosters erroneous feelings of skill and achievement.
Feeling as if you achieved something difficult enhances the satisfaction you get from winning at gambling. Chasing this sense of self-satisfaction and accomplishment can keep people playing games for hours, waiting for their moment of glory.
Avoiding Regret
The feeling of regret adds another layer to the already complex neuroscience of gambling. One study analyzed brain activity when gambling by looking at the short period between making a wager and learning the outcome of our bet. In this split second, gamblers’ brains are frantically replaying the previous betting decisions.
As these memories of previous bets play through our minds, people recall the feeling of regret from losing prior bets as well as the feeling of regret from not betting more on wagers won. This rapid replay of past betting experiences can result in apathy toward risk and willfully neglecting negative consequences in hopes of avoiding the regret that comes from missing out on a big win.
Casinos can play off of these emotions by incorporating more near misses into their game designs. Framing losses as if they were almost wins strings compulsive gamblers along by convincing them they will regret it if they stop playing at that moment. The fear of missing out on a jackpot overshadows the fear of potential negative outcomes and the player remains tied to the game.
Learn More About Problem Gambling at Gateway Foundation
Now that you know the brain activity associated with pathological gambling and how addicting casinos are designed to be, you can understand the dangers of compulsive gambling. Although a gambling addiction stands out as one of the few misuse disorders that does not involve consuming a substance, gambling disorder is still an isolating and solitary condition, just like any other form of addiction.
If you or someone you know struggles with pathological gambling, you are not alone. Gateway Foundation offers gambling addiction services designed to help anyone with a gambling disorder address the issue and get on the path to recovery. We provide cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication and support group options to help individuals conquer compulsive gambling.
For more information about pathological gambling or to get help with problem gambling, contact Gateway Foundation today.